Math 121 - Calculus for Biology I
Spring Semester, 2004
Product Rule - Examples
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 04-Jan-04
|
|
Math 121 - Calculus for Biology I |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 04-Jan-04 |
|
Differentiation of Functions with a Product
Example 1: Consider the function
Find the derivative of f(x) by using the product rule. Next multiply the terms in f(x), then take the derivative of the resulting polynomial. Show that these give the same functions, verifying the product rule.
Solution: The product rule is carried out by multiplying the first term times the derivative of the second term, plus the second term multiplied by the derivative of the first term.
We should be able to obtain the same result by multiplying the terms in f(x) and then taking the derivative of the resulting polynomial.
Thus, it is easy to see that the two methods do indeed yield the same result.
Example 2: Consider the function given by
Find the derivative of g(x) by using the product rule.
Solution: Again we multiply the first term times the derivative of the second term and add the second term multiplied times the derivative of the first term. Recall that the derivative of the natural logarithm equals the inverse of the argument.
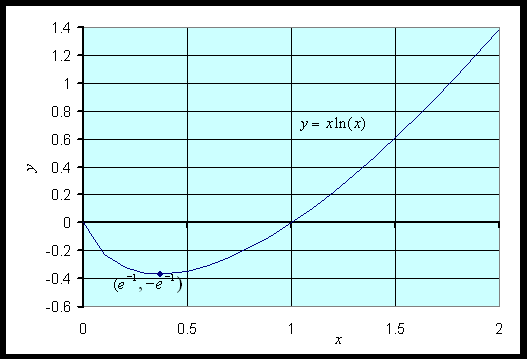
Example 3: Consider the function given by
Determine the domain of the function and find any intercepts. Find any critical points, then sketch the graph of f(x) for 0 < x < 2.
Solution:
ln(xc) = -1 or xc = e-1 ~ 0.3679
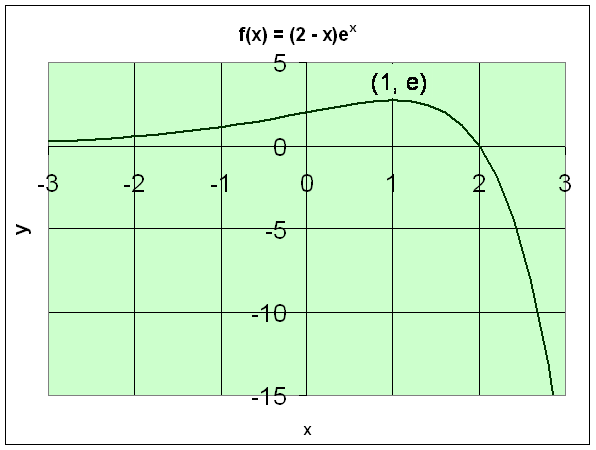
Example 4: Consider the function
f(x) = (2 - x)ex.
Solution:
f '(x) = (2 - x)ex + (-1)ex = (1 - x)ex = 0.
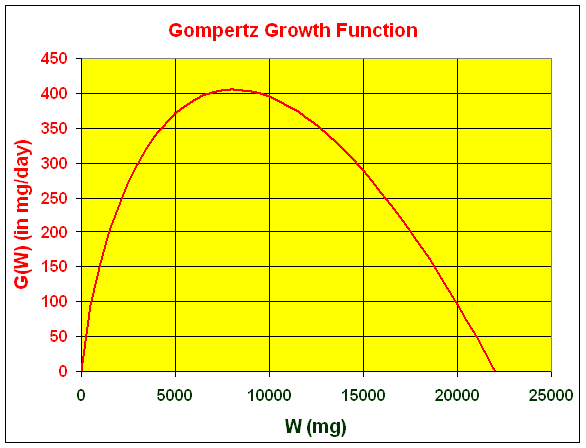
G(W) = W (0.5 - 0.05 ln(W)),
Solution:
G(W) = W (0.5 - 0.05 ln(W)) = 0
0.5 - 0.05 ln(W) = 0
ln(W) = 10
W = e10 = 22,026 mg.
G '(W) = W (- 0.05 (1/W) + (0.5 - 0.05 ln(W))
G '(W) = 0.45 - 0.05 ln(W) = 0.
ln(W) = 9
W = e9 = 8,103 mg.
G(8,103) = 8,103(0.5 - 0.05 ln(8,103)) = 405.2 mg/day.