|

|
Math 121 - Calculus for Biology I
Spring Semester, 2004
Applications of the Derivative - Examples
|
|
|
|
© 2001, All Rights Reserved, SDSU
& Joseph M. Mahaffy
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 02-Jan-04
|
|
 Applications of the Derivative - Examples of
Applications of the Derivative - Examples of
Stability of Discrete Models and Graphing
- Graphing Polynomials
- Height of a Ball
- Population Study
Examples
of Graphing Problems:
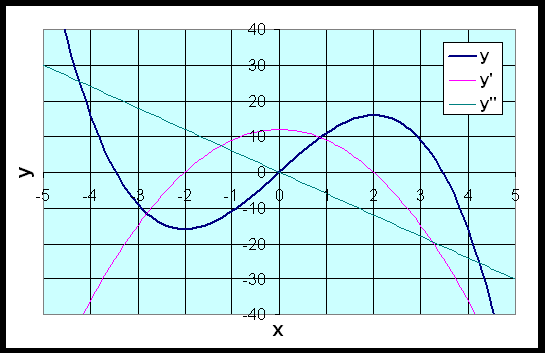
Example 1:
Find the local or relative minima and maxima and points of inflection
for the polynomial:
y
= 12x -
x3
Sketch a graph of the function.
Solution:
- The y-intercept is (0, 0)
- The x-intercept satisfies
y =
0, so
-x(x2 - 12) = 0
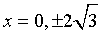
- For extrema, set the first derivative equal
to zero
- This gives the critical points xc
y'
= 12 - 3x2 = -3(x2 - 4) = -3(x
+ 2)(x - 2) = 0
xc = -2, 2
- Evaluate the original function at the critical
points gives
y(-2)
= -16 and y(2)
= 16
- The critical points of the function are
(-2, -16)
and (2, 16)
- Clearly, the first point is a minimum and the second is a maximum
y''
= -6x
y''(2) = -6(2) = -12 is concave downward, which indicates
a maximum
y''(-2) = -6(-2) = 12 is
concave upward, which indicates a minimum
- The point (-2,
-16) is a local minimum, and the point
(2, 16)
is a local maximum
- The point of inflection occurs where the
second derivative is zero
- The inflection point is at x = 0
- This means that the concavity direction
changes at point (0, 0)
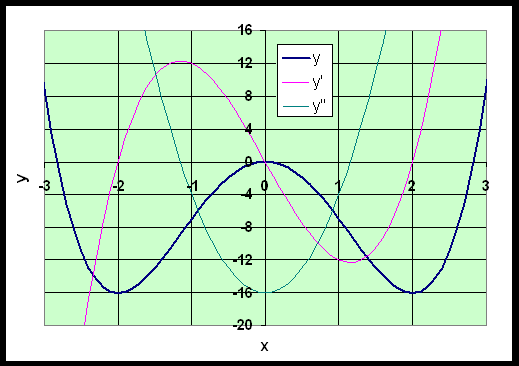
Example 2:
Find the local or relative minima and maxima and points of inflection
for the polynomial:
y
= x4
- 8x2
Sketch a graph of the function.
Solution:
- The y-intercept is (0, 0)
- The x-intercept satisfies
y =
0, so
x2(x2 - 8) = 0
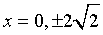
- For extrema, set the first derivative equal
to zero
- This gives the critical points xc
y'
= 4x3 - 16x = 4x(x2 - 4) = 4x(x - 2)(x
+2) = 0
xc = -2, 0, 2
- Evaluate the original function at the critical
points gives
y(-2)
= -16, y(0)
= 0,
and y(2)
= -16
- The critical points of the function are
(-2, -16),
(0, 0),
and (2, -16)
- Clearly, the first point is a minimum, the second is a maximum,
and the third is a minimum again
y''
= 12x2 - 16
= 4(3x2 - 4)
y''(-2) = 4[3(-2)2 - 4] = 32 is concave upward,
which indicates a minimum
y''(0) = 4[3(0)2
- 4] = -16 is concave downward, which indicates
a maximum
y''(2) = 4[3(2)2
- 4] = 32 is concave upward,
which indicates a minimum
- The point (-2,
-16) is a local minimum, the point
(0, 0)
is a local maximum, and the point (2,
-16) is a local minimum
- The point of inflection occurs where the
second derivative is zero
y''
= 12x2 - 16 = 4(3x2 - 4) = 0
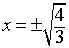
- The inflection points are approximately
x = (±1.155,
-8.889)
- This means that the concavity direction
changes at these points
Example
3: Height of the Ball Revisited
- A ball is thrown vertically
- Initial upward velocity of 64 ft/sec (v0= 64)
- Acceleration due to gravity is g
= 32 ft/sec2
- Find how high this ball travels
- The height function being a quadratic, so the vertex of
the parabola is the top of the flight of the ball
- Also, at this maximum
for flight of the ball, its flight the ball is temporarily stopped
- The velocity is zero at the time of the maximum height
of the ball
- The height of the ball satisfies
h(t) = 64 t - 16 t2
- The velocity function from differentiation is
v(t) = 64 - 32 t
- The velocity is zero at t
= 2 sec
- The maximum height of the ball is
h(2)
= 64(2) - 16(2)2 = 64 ft
Example
4: Study of a Population
- The ocean water is monitored for fecal contamination by
counting certain types of bacteria in a sample of seawater
- Over a week where rain occurred early in the week, data
were collected on one type of fecal bacteria
- The population of the particular bacteria (in thousand/cc),
P(t), were best fit by the cubic polynomial
P(t) = - t3 + 9 t2 - 15 t
+ 40,
a. Find the rate of change in population per day, dP/dt.
What is the rate of change in the population on the third day?
b. Use the derivative to find when the relative minimum and
maximum populations of bacteria occur over the time of the survey. Give the
populations at those times. Also determine when the bacterial count is most
rapidly increasing.
c. Sketch a graph of this polynomial fit to the population
of bacteria. When did the rain most likely occur?
Solution:
a. The rate of change in population per day is
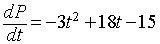
- Evaluating this on the third day
P
'(3) = 12 (x1000/cc/day).
b. For critical points, set the derivative equal
to zero
P
'(t) = -3 t2 + 18 t - 15 = -3(t - 1)(t - 5) = 0.
- The critical values are tc = 1or 5
Minimum
at t = 1 with
P(1) = 33 (x1000/cc)
Maximum
at t = 5 with
P(5) = 65 (x1000/cc).
- The bacteria is increasing most rapidly when the second
derivative is zero
P
"(t) = -6 t + 18 = -6(t - 3) = 0.
- The population is increasing most rapidly at t
= 3 with P(3)
= 49 (x1000/cc)
- This maximum increase is
P
'(3) = 12 (x1000/cc/day).
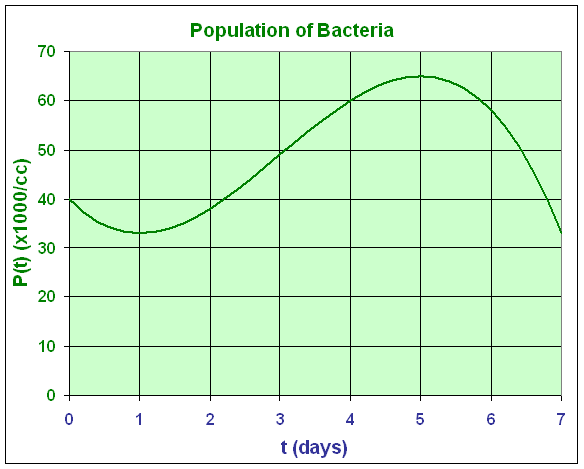
c. Below is the graph of this population
- Notice that the population at t
= 7 with P(7)
= 33 (x1000/cc),
which matches the local minimum given above
- From the graph, we can guess that the rain fell on the second
day of the week with storm runoff polluting the water in the days following

![]()

![]()
